RBI increased repo rate by 25 basis point. this is the latest update after February Monetary Policy Committee meeting. RBI take this decision to control the inflation rate of the country. which is currently remained above the tolerance range. In this article we learn about how repo rate control inflation of country.
After the 25 bhp in repo rate, the interest rate affect from 10 to 15 basis point according to high official of Banking sector. Govt main aim is ho to control this inflation as soon as possible. So the main responsibility behind it is RBI. who takes necessary action according to current scenario.so the current hike of repo rate is the part of inflation control policy.
Current Repo rate,SDF,MSF,Bank rate.
The reason behind hike on repo rate is CPI measures The Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U) increased 6.5 percent over the last 12 months .while consumer price index (CPI) inflation of 4 per cent within a band of +/- 2 per cent, to support growth of nation. this is the main reason hike of 25 bhp.
| Repo rate | 6.25(Old) | 6.50(New) |
| SDF(standing deposit facility) | 6.0(Old) | 6.25(New) |
| MSF( marginal standing facility) | 6.50(Old) | 6.75(New) |
| Bank rate | 6.50(Old) | 6.75(New) |
Repo rate is also known as liquidity adjustment facility which is control liquidity of country during the inflation.
What is Repo Rate.
The Repo rate is the interest rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends money to commercial banks in the event of any shortfall of funds. It is an instrument of monetary policy used by the RBI to control inflation and regulate the money supply in the economy. A higher repo rate makes borrowing more expensive for commercial banks, leading to a decrease in credit supply.
Repo rate history 1998 to 2023
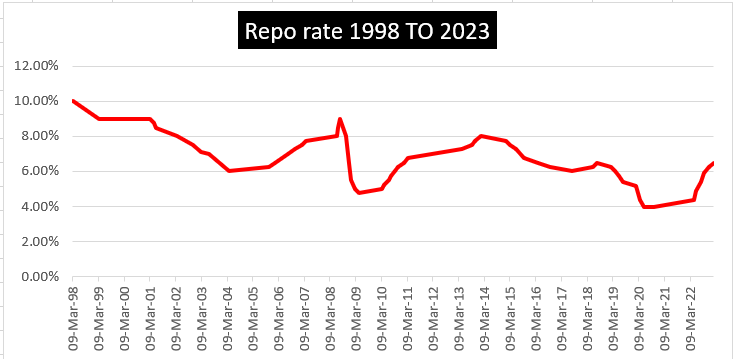
| Date | RBI Repo Rate | |
| 08-02-2023 | 6.50% | |
| 07-12-2022 | 6.25% | |
| 30-09-2022 | 5.90% | |
| 05-08-2022 | 5.40% | |
| 08-06-2022 | 4.90% | |
| 04-05-2022 | 4.40% | |
| 08-04-2022 | 4.00% | |
| 10-02-2022 | 4.00% | |
| 08-12-2021 | 4.00% | |
| 09-10-2021 | 4.00% | |
| 06-08-2021 | 4.00% | |
| 04-06-2021 | 4.00% | |
| 07-04-2021 | 4.00% | |
| 05-02-2021 | 4.00% | |
| 04-12-2020 | 4.00% | |
| 09-10-2020 | 4.00% | |
| 06-08-2020 | 4.00% | |
| 22-05-2020 | 4.00% | |
| 27-03-2020 | 4.40% | |
| 06-02-2020 | 5.15% | |
| 05-12-2019 | 5.15% | |
| 04-10-2019 | 5.15% | |
| 07-08-2019 | 5.40% | |
| 06-06-2019 | 5.75% | |
| 04-04-2019 | 6% | |
| 07-02-2019 | 6.25% | |
| 01-08-2018 | 6.50% | |
| 06-06-2018 | 6.25% | |
| 07-02-2018 | 6.00% | |
| 02-08-2017 | 6.00% | |
| 04-10-2016 | 6.25% | |
| 05-04-2016 | 6.50% | |
| 29-09-2015 | 6.75% | |
| 02-06-2015 | 7.25% | |
| 04-03-2015 | 7.50% | |
| 15-01-2015 | 7.75% | |
| 28-01-2014 | 8.00% | |
| 29-10-2013 | 7.75% | |
| 20-09-2013 | 7.50% | |
| 03-05-2013 | 7.25% | |
| 17-03-2011 | 6.75% | |
| 25-01-2011 | 6.50% | |
| 02-11-2010 | 6.25% | |
| 16-09-2010 | 6.00% | |
| 27-07-2010 | 5.75% | |
| 02-07-2010 | 5.50% | |
| 20-04-2010 | 5.25% | |
| 19-03-2010 | 5.00% | |
| 21-04-2009 | 4.75% | |
| 05-03-2009 | 5.00% | |
| 05-01-2009 | 5.50% | |
| 08-12-2008 | 6.50% | |
| 03-11-2008 | 7.50% | |
| 20-10-2008 | 8.00% | |
| 30-07-2008 | 9.00% | |
| 25-06-2008 | 8.50% | |
| 12-06-2008 | 8.00% | |
| 30-03-2007 | 7.75% | |
| 31-01-2007 | 7.50% | |
| 30-10-2006 | 7.25% | |
| 25-07-2006 | 7.00% | |
| 24-01-2006 | 6.50% | |
| 24-01-2006 | 6.50% | |
| 26-10-2005 | 6.25% | |
| 26-10-2005 | 6.25% | |
| 31-03-2004 | 6.00% | |
| 19-03-2003 | 7.00% | |
| 07-03-2003 | 7.10% | |
| 12-11-2002 | 7.50% | |
| 28-03-2002 | 8.00% | |
| 07-06-2001 | 8.50% | |
| 30-04-2001 | 8.75% | |
| 09-03-2001 | 9.00% | |
| 06-11-2000 | 10.00% | |
| 13-10-2000 | 10.25% | |
| 06-09-2000 | 13.50% | |
| 30-08-2000 | 15.00% | |
| 09-08-2000 | 16.00% | |
| 21-07-2000 | 10.00% | |
| 13-07-2000 | 9.00% | |
| 28-06-2000 | 12.25% | |
| 27-06-2000 | 12.60% | |
| 23-06-2000 | 13.05% | |
| 22-06-2000 | 13.00% | |
| 21-06-2000 | 13.50% | |
| 20-06-2000 | 14.00% | |
| 19-06-2000 | 13.50% | |
| 14-06-2000 | 10.85% | |
| 13-06-2000 | 9.55% | |
| 12-06-2000 | 9.25% | |
| 09-06-2000 | 9.05% | |
| 07-06-2000 | 9.00% | |
| 05-06-2000 | 9.05% | |
| 23-03-1999 | 9.00% | |
| 09-03-1998 | 10.00% |
What is SDF Standing Deposit Facility.
The Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) is a mechanism used by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for commercial banks to store their excess funds with the central bank for short periods of time. The SDF rate is the interest rate at which banks can deposit their excess funds with the RBI, and is usually lower than the repo rate. The use of the SDF helps commercial banks manage their liquidity and reduces their dependence on the inter-bank market for short-term funds. By offering a lower rate than the repo rate, the SDF also provides an incentive for banks to hold excess funds with the central bank rather than lend them in the inter-bank market, which can help reduce volatility in short-term interest rates.
Related…..How to Redeem ICICI Credit Card Reward Points.
What is MSF( Marginal Standing Facility)
The Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) is a scheme of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to provide overnight borrowing facilities to banks who are facing a temporary shortage of funds. The MSF rate is the rate at which banks can borrow money from the RBI, and is higher than the repo rate. The MSF is intended to be a penal rate, used only in exceptional circumstances when banks are unable to secure funds from other sources, such as the inter-bank market. By setting a higher rate for MSF compared to the repo rate, the RBI aims to discourage banks from regularly relying on this facility and encourage them to manage their liquidity more efficiently. The MSF is an very important tool for the RBI to manage short-term interest rates and to ensure the stability of the financial system.
What Is The Difference between the Repo rate and the MCLR rate?
Repo rate an instrument of monetary policy used by the RBI to control inflation and regulate the money supply in the economy. A change in the repo rate affects the borrowing costs of commercial banks and, in turn, the interest rates charged on loans to consumers and businesses.
And the MCLR is the minimum interest rate that a bank can charge for lending, set by each individual bank. The MCLR is calculated based on the marginal cost of funds, which includes the cost of borrowing funds from the RBI.
Read more…Indian Govt Announced New Income Tax Slab For FY 2023-24.
FAQ
Q. What is repo rate ?
Ans.The Repo rate is the interest rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends money to commercial banks in the event of any shortfall of funds. It is an instrument of monetary policy used by the RBI to control inflation and regulate the money supply in the economy.
Q. What is reverse repo rate.?
Ans. In Reverse Repo rate the Reserve Bank of India in case of India borrows money from commercial banks within the country. Repo rate greater then reverse repo rate.
Q. What is the main difference between repo rate and reverse repo rate?
Ans. Repo rate is the rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks, whereas reverse repo rate is the rate at which the RBI borrows money from commercial banks.
Q. What is MCLR?
Ans. Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate (MCLR) is the minimum interest rate at which a bank can lend.
Q. What types of loans are impacted by the Hike in repo rates?
Ans. A hike in repo rate can can impact the interest rates of Home loans, Personal loans, Car loans, Education loans , Corporate loans.
Q. How many times will banks can change loan interest rates that are tied to the repo rate?
Ans. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has introduced the Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate (MCLR) system, which requires banks to reset their MCLR at least once a year, and in some cases, on a monthly basis.
Q. How much is the current repo rate?
Ans. The current repo rate stands at 6.50%.
Q. How does repo rate affect the economy?
Ans. Repo rate, which is the rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks, has a significant impact on the economy. The RBI uses the repo rate as a monetary policy tool to control the money supply and manage inflation in the economy. Repo rate control these things ,Inflation control , Interest rates ,Currency value , Investment..

